Echo Cardiography
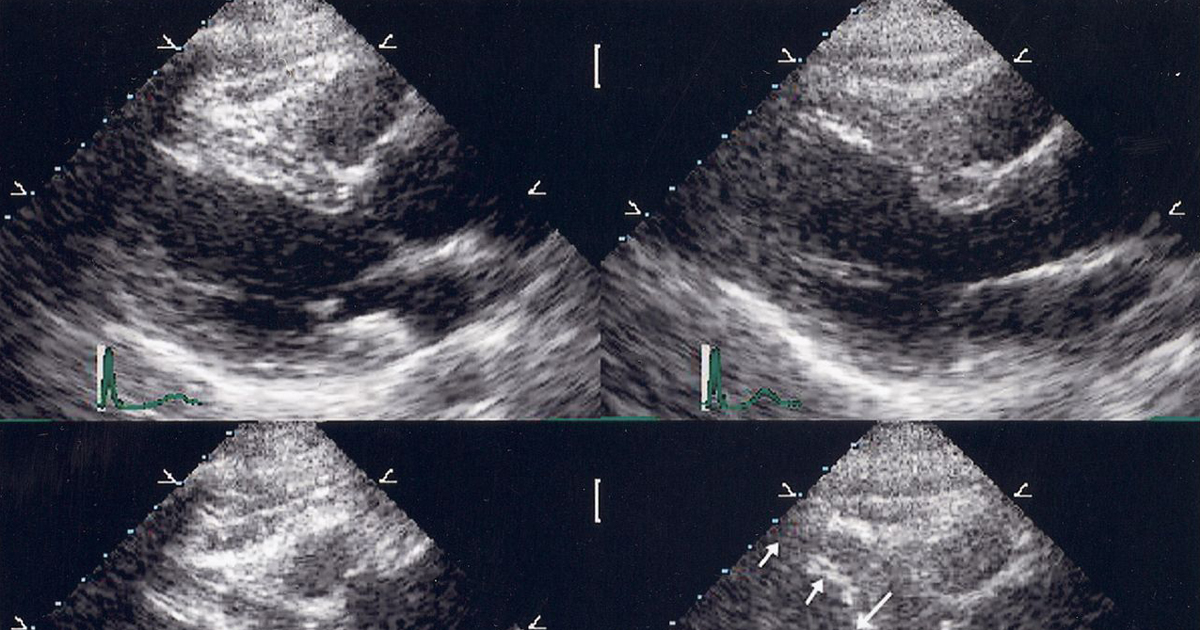
Echocardiography is a diagnostic test which uses ultrasound waves to make images of the heart chambers, valves and surrounding structures. It can measure cardiac output and is a sensitive test for fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion). It can also be used to detect abnormal anatomy or infections of the heart valves.
The heart is a two-stage electrical pump that circulates blood throughout the body. The anatomy includes four chambers and four valves. For the heart to function normally these structures need to be intact and the heart muscle needs to beat in a coordinated fashion, so that blood flows in and out of each chamber in the proper direction.
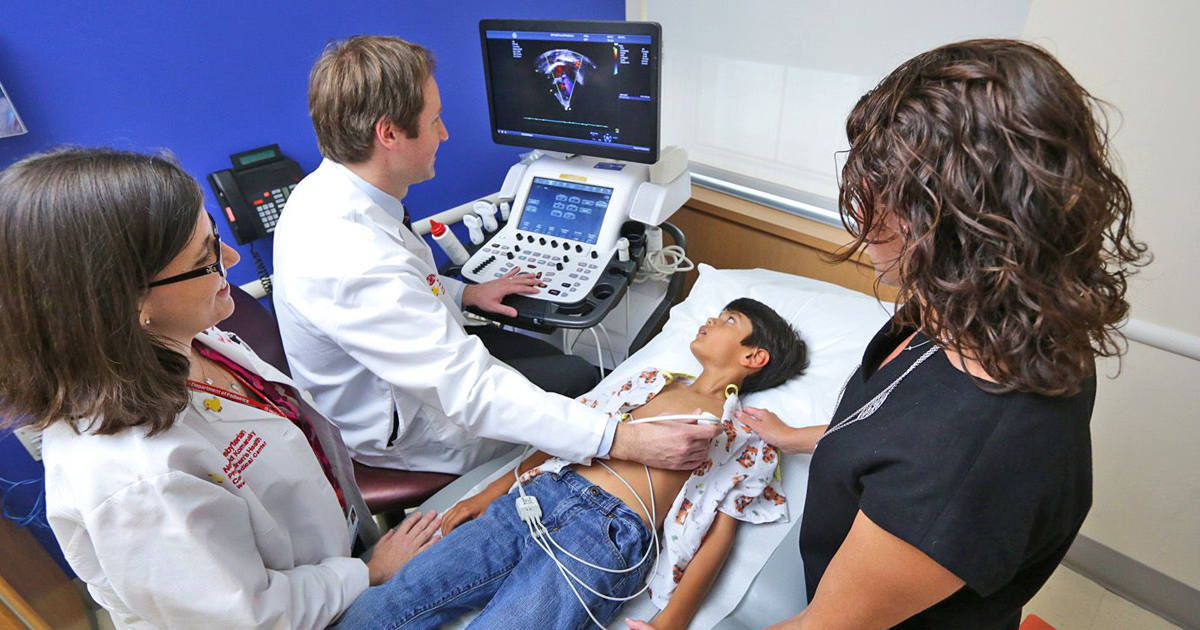
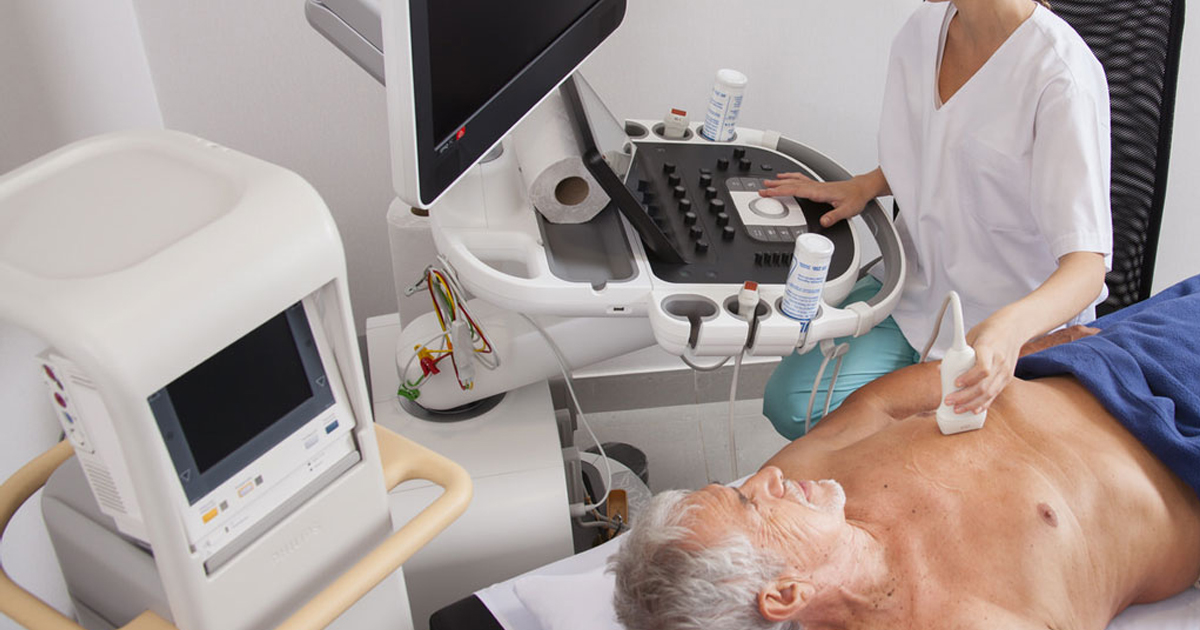
An echocardiogram (echo=sound + card=heart + gram=drawing) is an ultrasound test that can evaluate the structures of the heart, as well as the direction of blood flow within it. Technicians specially trained in echocardiography produce the images and videos, often using a special probe or transducer that is placed in various places on the chest wall, to view the heart from different directions. Cardiologists, or heart specialists, are trained to evaluate these images to assess heart function and provide a report of the results.The echocardiogram is just one of the many tests that can be done to evaluate heart anatomy and function.
An electrocardiogram (EKG, ECG) is the most common heart tracing done. Electrodes are placed on the chest wall and collect information about the electrical activity of the heart. Aside from the rate and rhythm of the heartbeat, the EKG can provide indirect evidence of blood flow within arteries to heart muscle and the thickness of heart muscle.